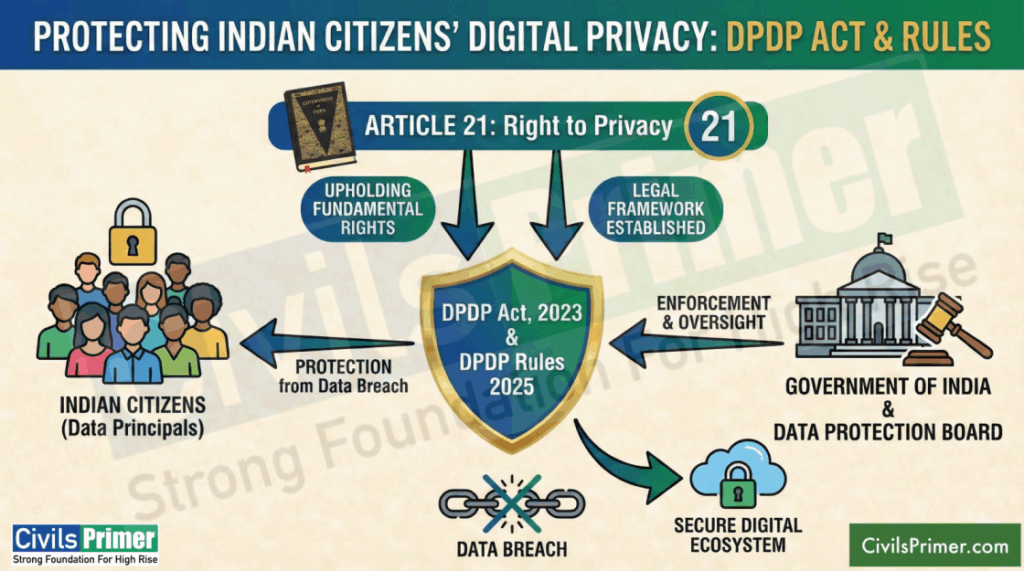
Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025: Decoding for UPSC Mains
Quick Summary: The Digital Personal Data Protection (DPDP) Rules, 2025 (notified 14 Nov 2025) operationalise the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023 — creating a rights-centric framework (consent, access, correction, erasure), a Data Protection Board, breach-notification rules and phased compliance timelines. Why UPSC candidates should care? (Syllabus Link): GS II (Polity & Governance): privacy as fundamental right (Puttaswamy Judgement), RTI interface, administrative adjudication (Data Protection Board), rule-making and executive power. GS III (Internal security / S&T / Economy): data governance, cyber-security obligations, impact on digital economy & AI/data-driven industry. Ethics & Essay: rights vs. state/market tradeoffs; accountability, transparency, checks &…